Bladder problems in women
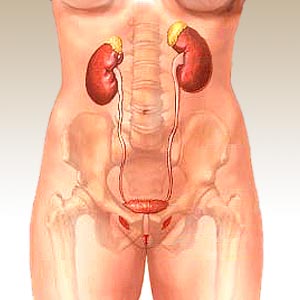
Many women are too shy or ashamed to talk about their bladder problems to anyone, including their doctor. So much so, that although ten million American adults, the majority of whom are women, have problems controlling their bladders, women continue to suffer in silence. Women of all ages suffer urine leakage. They are reluctant to seek treatment and relief.
Bladder problems faced by women include leaking urine, frequent urination due to overactive bladder and other symptoms of urinary incontinence. These bladder problems in women may be due to consequences of childbirth or a natural part of aging. However, several new techniques in the fields of urology and gynecology are offering succor to more and more women from bladder problems.
Common bladder problems in women
- Urine leakage - Most women experience incontinence. Women leak urine when they
exercise, laugh hard, cough or even sneeze. Pregnant women experience
urine leakage problems and women who have attained menopause also have
such bladder control problems. Due to strenuous sports activities, female
athletes of all ages sometimes suffer urine leakage.
- Urge incontinence occurs after a strong sudden urge
to urinate. This is a bladder control problem and can be due to nerve damage
from diabetes, stroke, infection or any other medical condition.
- Mixed incontinence is a combination of stress and
urge incontinence. There may be a
sudden uncontrollable urge to urinate before leak at another time.
- If there is urine leakage because of mobility
problems, it is functional incontinence.
- An overactive bladder is characterized by urination that
occurs eight or more time a day.
- Pain in the bladder, need to urinate and inability to
pass urine, progressively weak urine stream and inability to empty the
bladder completely are other bladder problems in women.
Overactive bladder in women
An overactive bladder is due to sudden involuntary contraction of muscle in the wall of the urinary bladder.
Overactive bladder causes sudden and unstoppable urgency to urinate. Overactive
bladder causes considerable social, psychological, occupational and sexual
problems among others. Frequent urination and urgency to urinate can be
construed as symptoms of this condition.
Causes for overactive bladder
Urinary incontinence can occur at any age and not necessary in the elderly. It should be understood that urinary
incontinence is not a disease. It is a medical problem and a doctor can help.
It is a symptom that can be caused by other conditions such as diabetes, stroke, multiple sclerosis and nerve diseases. Incontinence can worsen with aging, illness and injury. Overactive bladder may also develop as a complication of a nerve or brain related disease such as Parkinson's disease.
A vaginal or urinary tract infection or constipation can cause temporary bouts of urinary incontinence. Some medications are also prone to cause overactive bladder problems. Pregnant women suffer from overactive bladder temporarily caused by hormonal changes and pressure exerted by the growing fetus on the urinary tract.
Symptoms of overactive bladder
Urgency to pass urine and inability to put off going to the toilet is the most prominent symptom. There
is leaking of urine before she can get to the toilet. Frequency of urination,
more than seven times a day and more than twice during nights is another
symptom. Nocturia or walking to go to the toilet more than once at night is
another symptom of overactive bladder. Symptoms can get worse with stress.
Symptoms may also worsen with caffeine in tea, coffee, cola and alcohol.
Treatment for bladder problems in women
Statistics reveal that 8 out of 10 women who seek treatment for urinary incontinence show improvement or are
cured. Treatment options for overactive bladder depend much on the condition of
the patient. Some of the recommended line of treatments:
- Pelvic muscle rehabilitation is adopted to improve
pelvic muscle tone and prevent leakage of urine.
- Regular exercises can improve the pelvic muscle and prevent urinary incontinence especially
in younger women.
- Biofeedback is often used in conjunction with pelvic exercises to gain awareness and
control pelvic muscles.
- Vaginal weight training is a technique wherein small weights are held within the vagina
by tightening the vaginal muscles.
- Pelvic floor electrical stimulation helps in muscle contractions and should be done in
conjunction with other exercises.
- Regular exercises can improve the pelvic muscle and prevent urinary incontinence especially
in younger women.
- Behavioral therapies are adopted which can help her
gain control of the bladder. These help to resist the urge and gradually expand
the intervals between voiding.
- Certain medications may be used to improve
incontinence for overactive bladder. Estrogen, either oral or vaginal may be
useful in conjunction with other treatments for postmenopausal women. However,
these should be used only on advice from medical practitioner.
- Some general diet and life style measures can also
help in regulating an overactive bladder.
- Caffeine in tea, coffee, cola has a diuretic effect and stimulate bladder to make urgent
symptoms worse.
- It is recommended to stop intake of alcohol as the same principle of caffeine drinks
is applicable here also.
- Although some may think that it would be sensible to cut back the amount of fluid
intake, this is not recommended as the urine can become more concentrated and
cause irritation to the bladder muscle. It is advised to drink normal
quantities of fluids each day, usually about six to eight glasses of fluid and
probably more in hot weather.
- Caffeine in tea, coffee, cola has a diuretic effect and stimulate bladder to make urgent
symptoms worse.
- Bladder training called 'bladder drill' aims to
stretch the bladder to hold larger volumes of urine. In course of time, the
bladder muscle becomes less overactive and more bladder control is achieved.
- If the above treatments are not successful to treat
overactive bladder syndrome, surgery is resorted to. Surgical procedures that
may be used include:
- Sacral nerve stimulation where an implant in the bladder helps it contract more evenly
and normally.
- Augmentation cystoplasty is a procedure where a small piece of tissue from the intestine is
added to the bladder wall to increase the size of the bladder. People can pass
urine normally after this operation.
- Urinary diversion is an operation which directly routes the ureters to the bladder, outside the body such that urine does not flow into the bladder. This is done in various ways and this is adopted as a last resort if all other options have failed to treat an overactive bladder syndrome.
- Sacral nerve stimulation where an implant in the bladder helps it contract more evenly
and normally.
Top of the Page: Bladder problems in women
Tags:#bladder problems in women #overactive bladder in women
 Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction Bladder problems in women
Urinary Incontinence
UTI - Urinary Tract Infection
Feminine Hygiene
Yeast Allergy
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care
Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Women Health Directory
Top of the Page: Bladder problems in women
Popularity Index: 101,737

