Abdominal Hernia
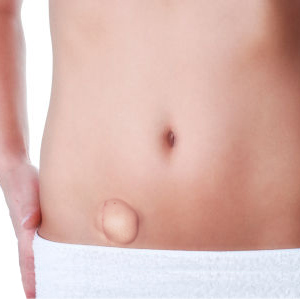
A lump in the abdomen, an uncomfortable pain in the groin area - could this be hernia? The term hernia is most often used to describe hernias of the lower torso, a lump in the abdomen. Reason being, most hernias occur when a piece of intestine slips through a weakness in the abdominal wall. The weakness in the abdominal wall could be congenital i.e. present at birth or acquired much later in life. Abdominal hernia can also be inherited.
Here is information about abdominal hernia, its causes, symptoms, and diagnosis. Find the basis which determines abdominal hernia repair. What determines the choice - abdominal hernia belt, abdominal hernia surgery or the abdominal hernia mesh? Check out advice given by Medical practitioners to prevent hernia from developing or recurring once more.
Abdominal hernia
Looking at the anatomy of human body, we know that the muscles are strong and tight enough to keep the intestines and organs in place. It is only when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes or pushes through a hole or a weak spot in the muscular structure of
the abdominal wall, abdominal hernia occurs. Abdominal hernias are classified
as either abdominal wall or groin hernias. It is the position or place which
decides the type.
Types of abdominal-wall hernia
Umbilical hernia
- Most common in infants but can affect adults also.
- Occur slightly more often in African Americans.
- Is a congenital malformation in babies, present since birth.
- Is due to obesity, pregnancy or excess fluid in the abdomen in adults.
- Umbilical hernia is usually painless.
- Develops in and around the area of the bellybutton (umbilicus).
- Symptoms-knot or bulge near the umbilicus.
- Hernia can occur any time from birth through late adulthood.
- Treatment required only when hernia continues past age 3 or 4.
- Medical attention must when hernia turns tender, discolored, swollen and/or when
the infant seems to be suffering from abdominal pain.
Epigastric hernia
- More common in infants but can occur in adults at any age.
- More common in men than in women.
- Cause is due to congenital defect or a weakness in the connective tissue or the
abdominal muscles.
- Develops in the middle of the upper abdomen between the breastbone and the umbilicus.
- Some epigastric hernias are visible and some others are invisible.
- Symptoms are belching, occasional vomiting and indigestion.
- Epigastric hernias are rarely harmful.
Spigelian hernia or lateral ventral hernia
- Men and women can develop this condition.
- Occurs in between the muscles found in the abdominal wall
- Outward evidence of swelling noticeable.
- Develops due to a weakening of the abdominal wall as a result of injury, sports
activities, abdominal fluid, post-surgery infection, prolonged periods of
physical stress etc.
- Symptoms include recurring pain followed by constant dull pain in the affected
area.
- Heredity too is a factor for an individual to develop spigelian hernia.
- Diagnosis involves physical examination, CT scan and ultrasonography.
Hiatus hernia
- Women are more prone when compared to men.
- Possibility high with advancing age and increasing weight.
- Newborn babies can develop congenital hiatus hernia.
- Small sized hiatus hernias have no symptoms.
- Symptoms for larger hiatus hernias are heartburn, acid taste in the mouth,
bloating, belching.
- Two types of hiatus hernia are sliding and rolling hiatus hernia.
- Endoscopy is the most common test for diagnosis.
Incisional hernia or ventral hernia
- Can occur after an abdominal surgery.
- May occur in men, women and children with prior surgery and an incompletely healed
wound.
- More common amongst adults than in children.
- The place is a weak area usually an incompletely-healed surgical wound.
- Symptoms are bulge or knot beneath the skin near the scar, sharp pains in
the abdomen and/or constipation.
- Cause is usually inadequate healing or excessive pressure on abdominal
wall scar.
- Develops after months or even years after surgery.
- Incisional hernias may or may not require surgical treatment.
Groin hernia includes inguinal hernia and femoral hernia.
Inguinal hernia
- Is the most common type of abdominal-wall hernia
- 98% occurs in men.
- Can occur at any age.
- Chances increases with advancement in age.
- Develops in the groin area.
- Symptom-A bulge in the groin or Scrotum, groin discomfort or pain.
- Cause is usually after effects of lifting heavy objects.
- Is sub-divided into direct and indirect inguinal hernia.
- Both sub-types occur in the groin area but with different origin.
- Both types appear similar.
- Diagnosis determines the sub-type.
Femoral hernia
- Less common than inguinal hernias.
- More common in women than in men.
- Develops in the groin area.
- Cause is usually the result of pregnancy and childbirth.
- Symptoms include discomfort or groin pain aggravated by bending or lifting and tender lump in the groin or upper thigh.
- Incidence rate highest in middle-aged and elderly women, especially women who have
had one or more pregnancies.
- Incidence is more of inguinal type in elderly women.
- Early diagnosis important to avoid complications.
Abdominal hernia symptoms
The primary hernia symptom is the lump in the lower abdomen or groin area. The
lump can be seen and felt as well. Yet, all lumps, protrusions or swelling in
the abdomen or groin area need not necessarily be a hernia symptom but could be
the result of an enlarged lymph node or any other abnormal growth. It is best
for the doctor to evaluate.
The lump may not necessarily be painful. Some hernias cause no pain at all. Often times, the presence of hernia is discovered during a routine medical check up. For some, the symptoms develop gradually. Additional symptoms may include the following.
- A bulge in the lower abdomen or groin area.
- Pain with lifting or coughing (Straining abdomen muscles)
- Changes in the bladder.
- Pain associated with straining during urination or bowel movement.
- Pain after prolonged sitting or standing.
- Discomfort and possible nausea
- Fever.
- Vomiting.
- Constipation
Abdominal hernia repair
Abdominal hernia symptoms should prompt a visit to the doctor.A physical examination is mandatory to confirm the presence of hernia. Sometimes ultrasonography, CT scans (computerized Tomography) or MRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging) help make the diagnosis. If any of the tests do not provide conclusive results,
diagnostic laparoscopy may be required.
As the first step, it is customary for the doctor to try and push back the lump (which is usually tissue or fat) into the abdominal cavity without causing any danger to the patient's health. On a case to case basis, the attempt proves to be successful. A lot depends on how far the lump is sticking through the abdominal wall and the intensity with which the abdominal muscles are holding it. If the attempt proves futile, a surgery will be recommended to repair abdominal hernia.
Umbilical hernia in infants goes away sans treatment within two years of age. In case, even after two, three or sometime four years, if the hernia persists, this large umbilical hernia will have to be repaired.
Other abdominal hernia types which can't be pushed back or reduced are most likely to be incarcerated or strangulated.
- An abdominal hernia which cannot be reduced is termed as irreducible or
incarcerated hernia.
- A strangulated hernia is an irreducible hernia in which a loop of intestine becomes tightly entrapped and the normal blood
supply to that part is cut off.
A hernia that has become incarcerated or strangulated is a medical emergency and abdominal hernia surgery has to be performed immediately. If the hernia is not incarcerated or strangulated, elective surgery which allows for repairing the abdominal hernia at a time convenient for the patient will be recommended.
Abdominal hernia surgery
Surgical repair of hernia is referred to as herniorrhaphy. Traditional and
laparoscopic are two different herniorrhaphy procedures. Successful
surgery serves three purposes. It repairs abdominal hernia, provides relief
from the associated discomfort and stops the hernia from progressing.
Traditional or open repair of abdominal hernia: Herein, a small incision is made over the hernia. Small hernias are most likely to be repaired by opting for traditional herniorrphaphy. The surgery is usually performed with local and intravenous sedation. After the surgery, the protruding tissue is returned to the abdominal cavity. A mesh will be attached over the weak spot in order to strengthen the wall of the abdomen.
Laparoscopic or closed repair of abdominal hernia: Smaller incisions, less pain and earlier return to normal activities - these are the three main benefits of opting for a minimally invasive procedure such as laparoscopic abdominal hernia repair. General anesthesia or spinal anesthesia will be administered to the patient. A laparoscopic device facilitates viewing the hernia on a monitor from inside the abdominal cavity.
Three small incisions are made. Through one incision, made under the patient's belly button, the laparoscope is inserted. Two other incisions are made in the lower abdomen to insert surgical instruments. Viewing images in the monitor, the doctor repairs the abdominal hernia. Mesh is then placed over the defect to reinforce the abdominal wall.
Abdominal hernia belt
A truss or hernia belt can be worn under the clothes.The abdominal hernia belts are removable, adjustable pads that help vary the pressure. It comes with straps which are useful to adjust the tension of the belt for comfort. They are available at drug stores and also at the doctor's offices. It is absolutely important to take doctor's advice and recommendation with regard to selecting abdominal hernia belt.
The belts do not cure abdominal hernia. The purpose of using an abdominal hernia belt varies from one patient to another. The belt can be worn prior to or after abdominal hernia surgery.
- To reduce pain and force back the lump into abdominal cavity.
- To lessen the uncomfortable feeling associated caused by the bulge or lump.
- To protect abdominal hernia repairs and prevent recurrence.
- To provide support/lessen damage till such time a convenient date for surgery is
fixed.
- To minimize appearance of the bulge, to keep the hernia from protruding.
- To gain personal confidence, improve appearance, security and carry on with
normal/routine activities minus any distraction.
Abdominal hernia care
Some types of abdominal hernia cannot be prevented. Steps can be taken to
avoid further complications and to prevent recurrence. The first step is to
learn about abdominal hernia and not indulge in activities that lay stress on
the abdominal wall.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects. If unavoidable make sure to use legs and not back
muscles.
- Use support braces while doing strenuous activities in order to avoid muscle
strain.
- Keep a tab on bowel movements. Bring it to the notice of doctor about constipation. It can be an indication of gastrointestinal disorder.
- Frequent coughing can be due to some allergy or pulmonary disease. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Post abdominal hernia repair, follow doctor's advice and lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Quit smoking, it weakens muscles and increases chances of developing
hernia.
Top of the Page: Abdominal Hernia
Tags:#abdominal hernia #abdominal hernia symptoms #abdominal hernia repair #abdominal hernia belt #abdominal hernia surgery #abdominal hernia mesh #epigastric hernia.
Causes of Stomach Ulcers
Abdominal Hernia
Internal Body Cleansing
Ulcerative Colitis
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Acid Reflux Syndrome
Belly Bloat
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Groin Hernia in Woman
Carcinoid
Colonoscopy Procedure
Bariatric Surgery
Hemorrhoids
Colon Cleansing
Other health topics in TargetWoman Women Health section:
General Women Health

Women Health Tips - Women Health - key to understanding your health ...
Cardiac Care
Women's Heart Attack Symptoms - Identify heart problems...
Skin Diseases
Stress Hives - Red itchy spots ...
Women Disorders
Endocrine Disorder - Play a key role in overall wellbeing ...
Women's Reproductive Health
Testosterone Cream for Women - Hormone replacement option ...
Pregnancy
Pregnancy - Regulate your lifestyle to accommodate the needs of pregnancy ...
Head and Face
Sinus Infection - Nearly 1 of every 7 Americans suffer from ....
Women and Bone Care
Slipped Disc - Prevent injury, reduce pain ...
Menstrual Disorders
Enlarged Uterus - Uterus larger than normal size ...
Female Urinary Problems
Bladder Problems in Women - Treatable and curable ...
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Causes of Stomach Ulcers - Burning feeling in the gut ...
Respiratory Disorders
Lung function Test - How well do you breathe ...
Sleep Management

Insomnia and Weight Gain - Sleep it off ...
Psychological Disorders in Women
Mood swings and women - Not going crazy ...
Supplements for Women
Women's Vitamins - Wellness needs...
Natural Remedies

Natural Diuretic - Flush out toxins ...
Alternative Therapy
Acupuncture Point - Feel the pins and needles ...
Top of the Page: Abdominal Hernia
Popularity Index: 101,732

